What is ORGANIC CHEMISTRY???
Carbon is the main constituent of organic compounds. It forms stable bonds with many other elements such as H, F, Cl, Br, I, N, P, S, etc. Carbon atoms form different types of structures depending on the number of carbon atoms.
These structures may be long chains of carbon, branched
chains, rings, chiral (optical property), or complex 3D molecules.
The Organic compounds are held together with the chemical bond linkage that is covalent bonding. Covalent bonding refers to the mutual sharing of electrons between different atoms.
The carbon atom has four
valencies that’s why it has the tendency to form four bonds and is sp3 hybridized. (more
about orbital hybridization)
The molecules or compounds that we study in Organic compounds are derived from natural or living resources. Moreover, these compounds are being used in our daily life as well as for medicinal purposes.
Complex organic substances can perform a wide range of biological tasks that are investigated in biochemistry. These complex molecules include vitamins, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, ATP, DNA, and RNA.
Importantly, the studies of natural products and their use are the major direction of research nowadays. So, to study organic chemistry properly, we need to understand the following aspects.
- The structural concepts and bonding in molecules
- Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)
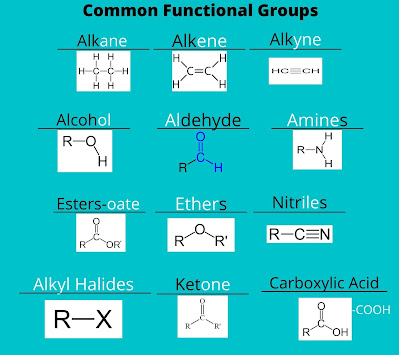
- Nomenclature of Organic compounds
- Mentioned below are the major rules for the nomenclature of organic compounds:
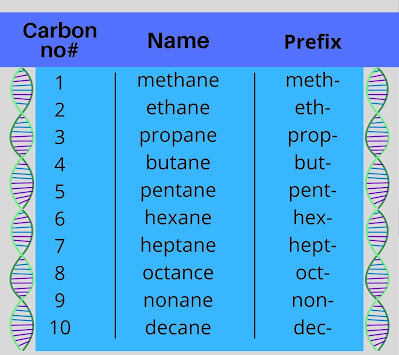
- First of all, we locate the longest chain of carbon atoms in the molecule
- We name the longest carbon chain by carbon atom using the prefix as shown below in the diagram.
- Identify the functional group and add suffixes.
- Identify the side groups by considering both sides of the carbon chain, and choose that side from where the side group approaches at first. The first carbon is considered the carbon with a side group presence.
- In the last, we have to name that side group, and here's the nomenclature done.
- Stereochemistry
The compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms in 3-dimensional space are known as stereoisomers.
There are two types of stereoisomers:
Diastereomers and Enantiomers.
Diastereomers
are superimposable mirror images, that are not enantiomers.
Enantiomers are
non-super-imposable mirror images. Or we can say that the chiral molecules with
are mirror mages of each other are enantiomers.
Meso forms
exist in molecules containing stereocenters that are symmetric/ achiral. Such compounds
and their mirror images are not stereoisomers, and are identical to each other,
these compounds are known as Meso compounds.
Some common terms used in stereochemistry:
Chiral carbon: The
carbon atom containing four different substituents attached to it. Also known
as Asymmetric carbon. Carbon is considered a common stereocenter/ chirality center.
Optical
activity: It is the ability of chiral compounds that can rotate the plane of polarized
light. If the plane of polarized light is rotated to the right it is Dextrorotatory.
Or if the plane of polarized light is rotated to the left it is Levorotatory.
Racemic
mixture: The mixture that contains equal amounts of enantiomers, has no
optical activity due to the presence of equal enantiomers.





Social Plugin