Physical chemistry-field study
Do you have any suspicions about how the things (matter) interact with each other??? Let me give you an introduction to physical chemistry to understand the interactions...
Let me introduce you to the branch of chemistry that purely explains how matter interacts with each other, its structure, and calculations. The laws and theories, explains the nature of atom, molecules, and compounds. As the name suggests it uses the theories and laws of physics to explain the interaction of molecules such as Boyles law, collision theory, etc.
Definition:
The Branch of chemistry that explains the interaction between molecules, their structure and physical properties on the basis of laws of physics and mathematical calculations is known as Physical chemistry.
It explains the reactivity of molecules/atoms in a chemical reaction, its occurrence, nature, and properties. Physical chemists are focused on understanding the chemical behavior of atoms as well as their structural properties.
Molecules with such exceptional properties are implemented in different fields. e.g., In industries, in the manufacture of medicine, electrochemistry, photochemistry, nuclear chemistry, food, preservatives, etc.
It is an area of interest to those chemists that love the deep study of atoms and molecules. It needs peace of mind to understand how things are happening. A person with a strong will to work in labs, handling and performing different experiments with instruments and machines. A basic understanding of mathematical calculations is a necessary thing.
Different fields are studied in the heading of Physical chemistry, such as;
- Chemical equilibrium
The state of reversible reaction where the rate of forwarding reaction becomes equal to the rate of backward reaction is coined as Chemical equilibrium.
CH3COOH +C2H5OH ó CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
This state is also known as the equilibrium state. The reversible reaction proceeds in both forward as well as backward reactions. And it is represented by a double-headed arrow. The concentration of reactants decreases as the reaction proceeds by the formation of products.
Hence the amounts of products increase in forwarding reaction. Eventually, when the equilibrium state is reached after some time the amount of product starts to decrease while reactants are reformed again.
Chemical equilibrium is dynamic in nature and there is no loss of reactants or products as the equilibrium state is established. Catalysts do not affect the reaction but it decreases the time of reaction to reach its equilibrium state.
There are two types of chemical equilibrium based on the state of matter (solid, Liquid, and Gases)
- Homogenous :
when the physical state of reactants or products is the same such equilibrium is known as homogenous equilibrium.
A(gas) ó B (gas)
A(liquid) ó B (liquid)
A(solid) ó B (solid)
A(g)+B(g) ó C (g)
- Heterogenous :
when the reactants and products in a chemical equilibrium
state have different/variety of physical states, such equilibrium is
Heterogenous equilibrium.
A(liquid)+B(solid) ó C (liquid)
A(g)+B(s) ó C (g) + D(g)
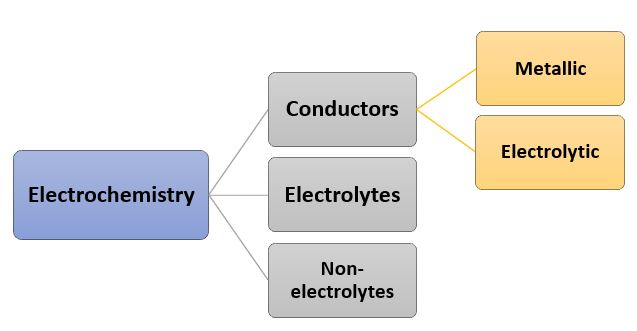
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with all physical and chemical processes due to the provision of electrical energy and it generates electricity as well.
The important content of electrochemistry involves,
Conductors are the substances that allow the current to pass through. Metallic conductors do not undergo any chemical change and all the current is transported by the electrons. Such conductors are also known as electronic conductors as the electrons carry the whole current.
The other conductors are electrolytic which involves the migration of ions that conduct the current and transport it. As the ions are positively and negatively charged, they move towards oppositely charged electrodes where chemical reactions take place.
The electrovalent substances that form ions when dissociated in solution and carry electric current are known as Electrolytes. While non-electrolytes do not carry electric current as these substances produce neutral molecules.
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics is the study of the rate of reaction and its mechanism. Here, the rate of reaction is the rate of change of concentration of reactants or products over time.
Rate of reaction = dx/dt (mol/dm3s)
The rate of reaction can be slow, medium, or fast. So, based on reactions rate, there are three types of reactions,
- Slow reactions:
For example, Rusting of iron
- Intermediate/moderate reactions:
ex. Decomposition of hydrogen iodide to hydrogen and iodine
- Fast/ instantaneous reactions:
The reaction of Acidified KMnO4 with FeSO4
solution, that results in decolorization.
Surface chemistry
The chemical reactions that take place on the surface interface are discussed in surface chemistry. The adsorption of molecules to a surface (solid/liquid, solid/gas, etc) through chemisorption or physisorption.
Matter and its physical properties
Anything that has mass and occupies some space is called matter, for example, solids, liquids, and gases. It involves the deep studies of matter, its physical properties, and its effects on the chemical nature of molecules.
Atomic structure and quantum theory
Understanding the structure of atoms, with the help of Rutherford and Bohr’s atomic model. The energy levels, their names, calculations, and distribution of atomic particles are studied in this field. Quantum theory is used to explain the presence of electrons with the help of quantum numbers. These four quantum numbers are;
- Principal quantum number
- Azimuthal quantum number
- Magnetic quantum number
- Spin quantum number
Spectroscopy
The study of electromagnetic radiations with matter is known as spectroscopy. There are different types based on the nature of light;
Thermodynamics
It refers to the transformation of heat and this heat can be transformed by three methods, Conduction; Convection; Radiation.
Pressure, volume, and temperature are considered thermodynamic variables that are used to express the state of matter. Entropy, enthalpy, internal energy, and Gibbs free energy depend on these variables.
Nuclear chemistry
It is the study of atomic nuclei. In nuclear reactions, the nucleus is involved and there is a change in the proton or neutron number of elements to form a new element. It is also regarded as radioactive chemistry because radioactive elements are involved in it and they release a very large amount of heat (energy). Such as fission and fusion reactions and chain reactions.
The radiations that are involved in this study are alpha,
beta, and gamma rays.
Symmetry of molecules
The symmetry of molecules involves understanding the structure of molecules by applying different symmetrical operations.
There are five symmetrical operations;
- Identity
- The proper axis of rotation
- Plane of symmetry
- Centre of symmetry
- The improper axis of rotation
Nano-chemistry
Nano-chemistry deals with the study of nanoparticles, their synthesis, properties, and applications. The Nano-materials can be natural or artificial based on occurrence. These materials have interesting catalytic, magnetic, optical, electric, and mechanical properties.
Physical-organic Chemistry
The study of organic molecules by utilizing the physical chemistry tool and strategies for determining the chemical structures, reactivity, and special properties.
Chemical kinetics
To determine the rate of reaction, molecularity, and the number of reactants used up in a chemical reaction to form the product. The use of a suitable catalyst that speeds up the chemical reaction and the effect of solvent w.r.t suitable substituents attached.
Spectroscopy
There are different types of spectrometry techniques that are used to identify electronic excitations, molecular mass, functional groups, magnetic/ paramagnetic behavior, etc of organic molecules.
These spectroscopic techniques are,
- UV-visible spectroscopy
- Infra-Red spectroscopy
- Mass spectroscopy
- NMR spectroscopy
Thermochemistry
Thermodynamics is used to study the stability and type of bonding between organic molecules. As well as the amount of energy absorbed or evolved by the system can be understood with the help of thermochemistry. Such determinations involve changes in enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy, and other chemical changes.
Physical-Theoretical chemistry
Physical chemistry is also called theoretical chemistry as it involves structural determination and analyzing their properties. Such molecular analysis is utilized to make drugs, molecular docking, products used in daily lives and industries, etc. theoretical chemistry involves,
- Designing of drugs
- Molecular docking
- Quantum mechanics
- Protein-protein docking
- Interpreting movements of nuclei
Theoretical chemistry involves many tools that involve computational software, numerical simulations based on quantum calculations, and mathematical derivations.
The utilization of computational software for determining and analyzing the structural properties of special compounds refers to Computational chemistry. It involves density functional theory (DFT) calculations which use quantum mechanics to understand the electronic structure of molecule via Gaussian software setup.





Social Plugin