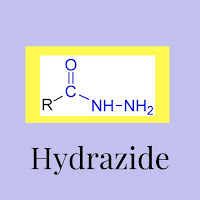
In Organic chemistry, the characterization of hydrazine is a class of organic framework. Hydrazides and their derivatives are of greater use in biological as well as economical industry.
In this Blog, you would be able to understand the properties and
applications of hydrazide and acetohydrazide as a perfect NLO material.
A common hydrazine core replaces a functional group of at least one hydrogen atom with an acyl group substitute.
The overall structure for hydrazides is E(=O)NRNR2, in which the R's are frequently hydrogens. The chemistry of the – C = N – group of hydrazides is the basis of the condensation reaction.
It also represents an important class of compounds used in producing new drugs.Acetohydrazides, also known as N-acyl hydrazones, are synthesized using Acid Catalysts using standard practices similar to those used for Schiff bases.
In this procedure, hydrazide is allowed to react with a substituted
aliphatic/aromatic aldehyde in the presence of acid as a catalyst.
Nearly all the syntheses of acetohydrazide derivatives have the
same technique. The synthesis of N-acyl hydrazones and their structural study
have gained Significant attention to the emergence of geometrical isomers and
biological properties in recent years, primarily because of their efficacy in
the synthesis.
The hydrazone group contributes to the nucleophilic and electrophilic character, which enhances their use in organic chemistry and the fabrication of new drugs.
Properties Of Hydrazide derivatives
Aromatic hydrazide derivatives are considered an effective inhibitor of corrosion in mild steel. These derivatives are helpful for various biological properties; hydrazides are valuable starting materials for a broad range of results that can be used in pharmaceutical products and as surfactants.
Hydrazides have been known to associate with antibacterial
activity. In addition, they are often used as potential inhibitors to combat
corrosion in many metals, including mild steel.
The examples of other organic acid hydrazides that were tested
for corrosion inhibition were salicylic acid hydrazide (SAH), anthranilic acid
hydrazide (AAH), and benzoic acid hydrazide (BAH), which have AOH, ANH2, and AH
respective replacements.
Acetohydrazide- a powerful derivative of hydrazides
Acetohydrazide derivatives are powerful anticancer, analgesic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiproliferative agents, inhibiting enzyme and antibacterial activity, and antidepressants.
Their ability to inhibit platelet
aggregation at the PAF receptor level was outstanding and proven to be a potent
antithrombic agent. In contrast, some more acetohydrazide surrogates are
reported to inhibit tumor necrosis factor activity.
The pyridine ring also improves the antitumor function by adding specific substituents, such as Thiazole, thiophene, benzothiophene, triazole, or pyrazole Cyanoacetohydrazide.
Applications:
Hydrazides and their derivatives have attracted considerable
interest due to various applications in the field of medicine, such as,
- antibacterial
- anti-inflammatory
- anticancer
- antiplatelet
- antimalarial
- analgesic
- antioxidant
Hydrazides and their analogs have been effectively used to
fabricate medicinal products such as anti-tuberculosis, antimicrobial,
antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet agents, anticonvulsants,
antioxidants, antimalarial agents, and anti-trypanosomal agents. In
particular, tuberculosis diagnosis requires isonicotinic acid hydrazide.
The Structural-Activity Relationship (SAR) of the compounds with
these rings is reported as an anticancer. Thiazolo derivatives portray
anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiparkinson, and anticonvulsant activity with
2,6-disubstitutedsotonic acid hydrazides.
In addition to their medicinal effects, these scaffolds have
been successfully entailed in organic reactions in the form of reactive
functional groups. In addition, hydrazides can be used as organo-catalysts in
several chemical transformations.
In the same way, hydrazides have acted as effective vasodilators
and hormone antagonists. These compounds are a big concern and inspiration for
medicinal chemistry due to the unknown biological potential associated with
such compounds.
Several acetohydrazide products demonstrate anti-HIV activity and
N-substituted thiosemicarbazide have antidiabetic potential. The new form
of acetohydrazide analogs is reported to have anti-inflammatory activity and
anti-thyroid movement.
They have also prevented mild steel corrosion in the acidic
medium. Gummadi and associates have reported several acetohydrazide that have
exhibited moderate to the strong antibacterial and antifungal activity.
Non-linear optical properties
Acetohydrazides are promising applicants for NLO materials among organic NLO molecules because these compounds contain an additional C = O site which induces an extensive p-electron.
The binding affinities with the protein by intermolar interactions and the delocalization of pi electrons are strengthened more extensively by adding different substituents in the aromatic rings.
The entire hydrazone fragment is delocalized. Since the backbone of the
hydrazone is an asymmetric charging transmitter, molecular nonlinearity for
electron withdrawing and donating groups is immensely increased.
Organic compounds often test and compare NLO materials with urea and NLO reaction molecules. Thus, hydrazides will appear as good NLO content due to their structural similarity to urea.
The research community has focused
on developing new derivatives to achieve great medicinal and biological
applications for such molecules.





Social Plugin